From data transfer and power delivery to connecting external accessories, USB-C has become a universal standard in modern electronics. In the broad Xiaomi ecosystem, from budget-friendly Redmi devices to flagships such as Xiaomi and Pad series, the role of the USB-C port is very different. Although it is the same physical connector, its real functions vary significantly depending on the model and internal hardware protocols.
One of the things this article will do is look into the real technical potential of the USB-C interface in Xiaomi phones and tablets: charging, data transfer, display output, and audio performance. This analysis is based on Xiaomi’s hardware segmentation and finds out why not every port labeled “USB-C” offers the same power.
Power and Charging: The Core of Xiaomi’s USB-C Strategy
HyperCharge vs. Universal Standards
Thus, HyperCharge technology by Xiaomi represents one of the fastest proprietary charging systems going up to 120W, 90W and 67W. It relies on the brand’s exclusive Xiaomi PPS protocol, which requires a safe digital “handshake” between the phone and its original charger. Most third-party chargers, even high-power ones, often deliver only basic 10W speeds when this kind of handshake fails.
The system works at top efficiency only with official Xiaomi cables and adapters, effectively making ultra-fast charging a function of the Xiaomi ecosystem. This is a safety and a branding decision in one, making sure that performance is reliably consistent while encouraging users to favor official accessories.
Universal Compatibility and Fallback Protocols
Despite this proprietary lock, Xiaomi devices do remain compatible with Power Delivery (PD) and Quick Charge (QC) standards. For example, models such as the Xiaomi Pad 6 or Mi 9 SE support PD 3.0 and QC 4.0. Similarly, on non-Xiaomi chargers, they can achieve a moderate fast-charging speed of 18-33 W, assuming negotiation is successful.
Reverse Charging and OTG Functionality
Most Xiaomi phones support reverse wired charging, which lets them act as a temporary power bank. Devices can power accessories like earphones, wearables, or even other smartphones using a USB-OTG adapter. However, direct USB-C-to-USB-C connections without an OTG handshake may cause unpredictable charging direction and are hence not recommended.
Data Transfer: Why Most Xiaomi Phones Are Stuck on USB 2.0
The Performance Gap
While USB 3.x can reach speeds of up to 5 Gbps, several models from Xiaomi, like the Xiaomi 13 Pro, are still on USB 2.0, which reaches a maximum of 480 Mbps, or roughly 35–40 MB/s. These lead to rather long transfer times for big files. For instance, the transfer of a 20 GB 4K video takes more than 10 minutes using USB 2.0 but less than one minute with USB 3.2.
Premium Models with USB 3.2
Only high-end devices, such as the Xiaomi 14 series and the Pad 6 series, receive USB 3.2 Gen 1 (5 Gbps), and use of these faster ports enhances not only file transfer speeds but also unlocks DisplayPort Alternate Mode required for wired video output.
The Future: USB4 Accessories
While Xiaomi sells USB4 Gen 3 cables that support up to 40 Gbps speeds and 240 W PD 3.1 charging, no Xiaomi smartphone supports this protocol. These accessories are likely designed for future devices such as the Xiaomi 15 or newer laptops.
USB-C supports video output. But is that actually true?
Why Most Xiaomi Phones Can’t Output Video
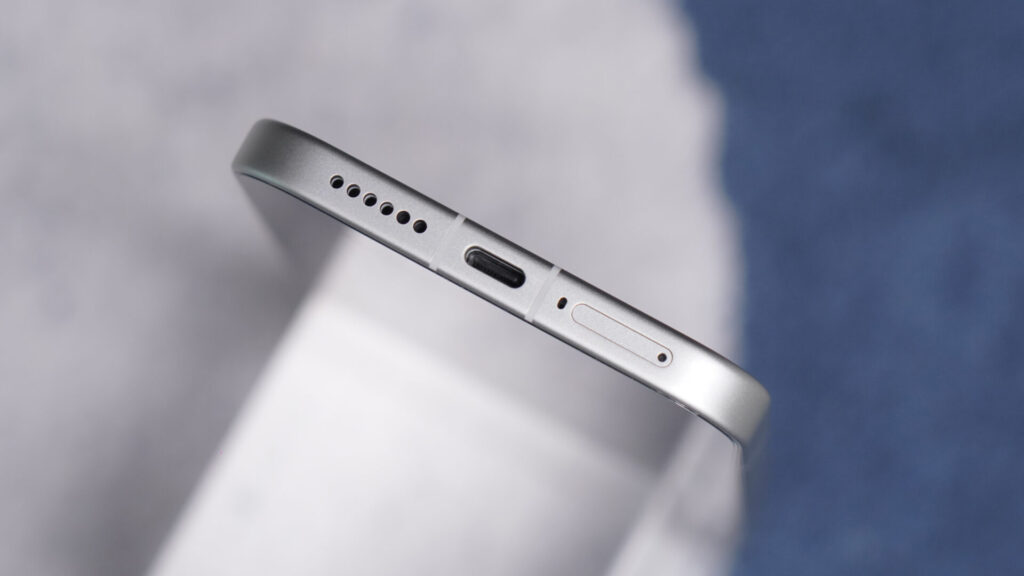
The reason why a Xiaomi phone cannot be connected to a monitor using a USB-C to HDMI cable does not involve software issues, but rather is related to hardware limitations. Only devices with DisplayPort Alternate Mode-available on USB 3.x-enabled ports-can output the video signal.
Confirmed models supporting DP Alt Mode include:
- Xiaomi 13 Ultra
- Xiaomi 14 series
- Xiaomi 15 series
- Xiaomi 17 series
- Xiaomi Pad 7 series
For instance, phones like Redmi Note 13 Pro or Xiaomi 13 Pro, even with USB-C, don’t have the needed wiring for DP Alt Mode to provide native video output. DisplayLink adapters can still be used, but these provide compressed, laggy visuals unsuitable for gaming or streaming.
Workstation Mode on HyperOS Tablets
On Xiaomi Pads, the USB-C port supports “Workstation Mode,” enabling windowed multitasking similar to Samsung DeX. However, reports indicate that this feature mirrors the screen instead of enabling a full desktop environment. It suggests Xiaomi’s proprietary interface currently overrides Android’s native desktop mode.
Audio Output: Digital, Analog, and DAC Integration
How Xiaomi handles USB-C audio
With the majority of Xiaomi devices giving up the 3.5 mm jack, USB-C has become the main audio interface. The port can operate in **two modes:
- Digital mode: sound is processed by an external DAC (which resides either inside the adapter or in the headset).
- Analog mode, where Xiaomi’s internal DAC handles audio before output
The DAC Dilemma
Tests on the Xiaomi Pad 6 show that using a simple DAC-less adapter yields higher sound quality than premium adapters with built-in DACs (like Samsung’s). This proves that Xiaomi integrates a high-quality internal DAC, which external adapters may unintentionally bypass. For optimal results, users should prefer official or basic DAC-free Type-C to 3.5 mm adapters.
Xiaomi’s USB-C is far more involved than it seems. The same connector can offer 120 W charging, 5 Gbps data, video output, or hi-res audio—depending on the model. The port has become a tool of ecosystem segmentation, balancing universal compatibility with proprietary optimization. These distinctions are important to understand to make smarter accessory choices and appreciate how Xiaomi engineers extract the maximum performance from a single port.



 Emir Bardakçı
Emir Bardakçı






I have usb-c to hdmi in Xiaomi Pd 6S pro. When i connect an HDMI cable to an externl monitor it asks rigth way if it want to mirror.
“On Xiaomi Pads, the USB-C port supports “Workstation Mode,” enabling windowed multitasking similar to Samsung DeX. However, reports indicate that this feature mirrors the screen instead of enabling a full desktop environment. It suggests Xiaomi’s proprietary interface currently overrides Android’s native desktop mode.”
Yeah Xiomi worstation mode is basicaly useless. Very poor implementation and unfortunately not surprising from Xiaomi.