In a major development in the Android space, Google officially ended the support of Android 12 and Android 12L systems, ending the life of the systems that supported millions of handsets globally. This move will result in these systems no longer getting security patches, leaving them at risk of new threats if they are not upgraded to newer versions of Android. It comes at a time when Xiaomi is leading the market in its frequent update cycles, extensive security protocols, and stellar long-term support of its wide range of handsets.
End of the Road for Android 12
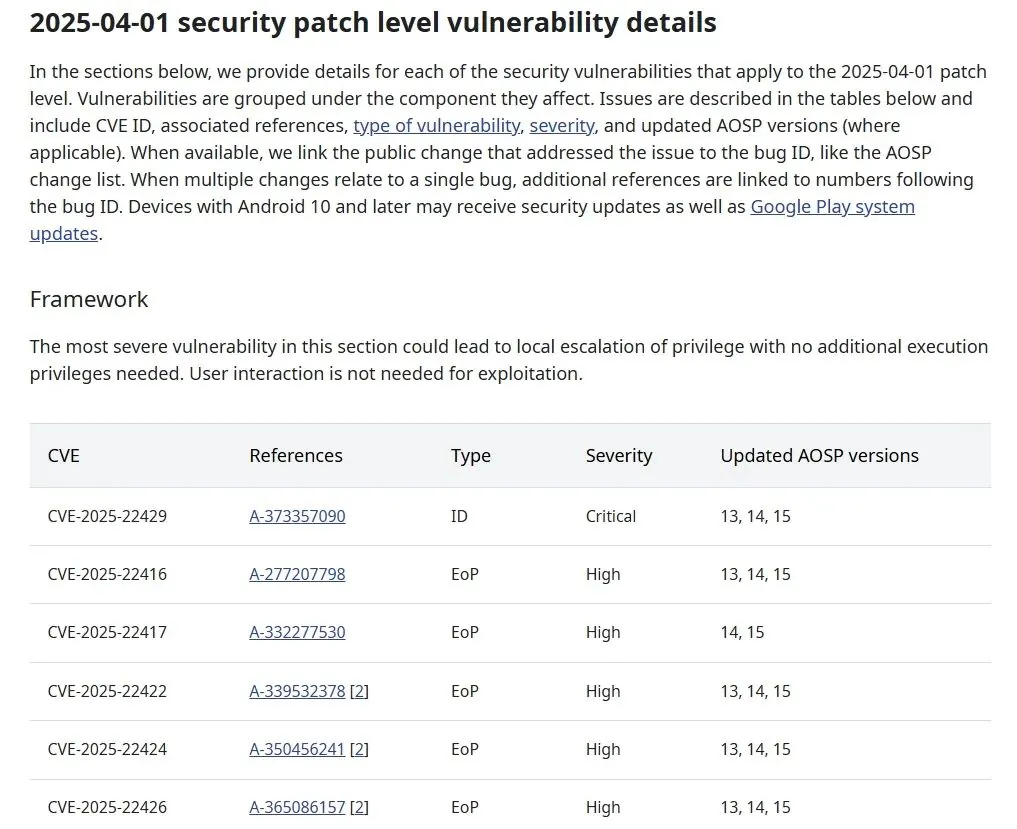
As per a report published recently by Android Authority on April 15, 2025, Google removed Android 12 and Android 12L from its current security bulletin. March 31, 2025, was the official end-of-life date of the two versions, ending their support life span after about:
- 3.5 years for Android 12 (launched October 4, 2021)
- 3 years for Android 12L (launched March 7, 2022)
This is consistent with Google’s corporate standard of offering security patch support on a system for about 3.5 years following the system’s initial release date
Impact on mobile device manufacturers
The end of official support presents tremendous challenges to device makers who are currently supporting Android 12 handsets. Without the security fixes provided by Google, manufacturers have two hard choices:
- Indigenously develop and port security patches
- Unplug devices that lack essential security updates
For low-resource manufacturers, it is usually not feasible to individually secure these systems, and so many systems are left exposed and unprotected.
Security Implications to the User
This change presents significant security issues to users who are currently using Android version 12 or version 12L:
- Unannounced vulnerabilities addressed in more recent versions won’t get backported
- Devices can leave themselves open to security vulnerabilities that have previously been rectified by Google engineers
- Updates will keep coming to Google apps and Project Mainline modules, but core system vulnerabilities will not get patched
Google also ceased signing new Android 12-based builds, effectively ending the update life cycle of those versions altogether.
Recommendations to Android 12 Users
For those who are using Android 12 or 12L, security professionals prescribe:
- If possible, upgrade to a newer Android version
- Investing in a device replacement if not available
- Recycling obsolete equipment for less sensitive uses such as video players or security cameras
- Refrain from the utilization of outdated equipment for banking, personal communication, or the storage of personal data
Xiaomi customers are availing themselves of the company’s dedication to delivering timely upgrades to its device base, simplifying the upgrade to newer, more secure versions of Android.


 Emir Bardakçı
Emir Bardakçı