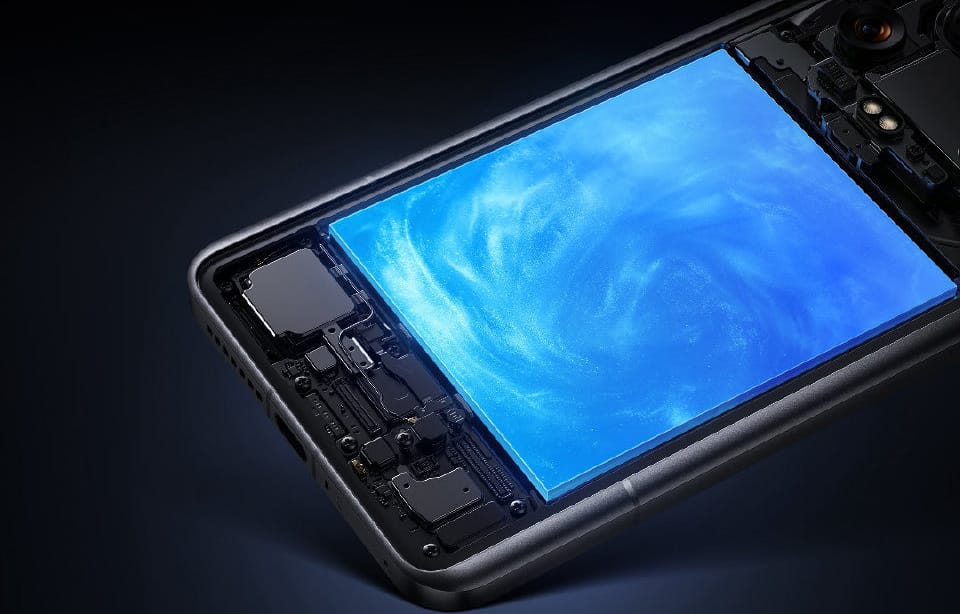
As mobile performance skyrockets with power-hungry chipsets like the Snapdragon 8 Elite and ultra-bright displays, standard lithium-ion batteries are struggling to keep up. To solve this, Xiaomi introduced the Jinshajiang (Golden Sands) battery, a high-density energy storage technology paired with Xiaomi HyperOS, already powering new Xiaomi, REDMI, POCO series such as Xiaomi 17 and upcoming POCO X8 Pro.
What is Xiaomi Jinshajiang Battery Technology?
The Xiaomi Jinshajiang battery is an advanced power cell utilizing a Silicon-Carbon (Si-C) anode instead of traditional graphite. This allows Xiaomi to significantly increase battery capacity and energy density without making the smartphone thicker.
Traditional batteries rely on graphite-based lithium technology. However, the Jinshajiang battery upgrades to a Silicon-Carbon (Si-C) anode material. While silicon can absorb significantly more lithium ions than graphite, it historically suffered from expansion issues during charging.
Xiaomi successfully overcame this barrier by mixing nano-sized silicon particles with a stable carbon structure. By carefully controlling the silicon levels—keeping it optimized for smartphone stability while allowing higher concentrations in accessories like power banks—Xiaomi achieved a slimmer, safer, and higher-capacity battery.
Key features of the Jinshajiang battery
-
Higher volumetric energy density than traditional graphite batteries.
-
Longer lifespan through highly controlled silicon expansion.
-
Full compatibility with existing lithium-ion production infrastructure.
-
Market-ready integration for ultra-thin foldables and flagship smartphones.
Self-Healing Electrolytes: Why Does a Xiaomi Battery Degrade?
If you ever asked yourself “why does a Xiaomi battery degrade over time?”, the answer lies in the micro-cracks that form inside standard batteries during charging cycles. Xiaomi solves this by using self-healing electrolytes that repair these cracks, extending battery lifespan far beyond industry standards.
Battery health naturally declines over time due to wear and tear at the chemical level. During regular charging cycles, micro-cracks form at the interface of the anode and electrolyte materials, permanently reducing capacity.
To combat this degradation, Xiaomi incorporated elastic polymer additives into the Jinshajiang battery’s liquid electrolyte. These additives dynamically adjust to the volume expansion of the silicon. If small defects or cracks arise, the electrolyte interface actually recovers and heals itself. Thanks to this self-healing mechanism, Xiaomi batteries can maintain 80% capacity even after 1,600 charge cycles, providing years of peak performance, even with frequent fast charging.
Xiaomi still testing better battery tech than Si-C batteries: Xiaomi Solid-State Battery
While the Jinshajiang battery is today’s solution, Xiaomi solid-state batteries are the future. By replacing flammable liquid electrolytes with solid materials, these upcoming batteries promise massive energy density (over 1,000 Wh/L) and extreme safety for both phones and electric vehicles.
While Jinshajiang cells are currently in mass production, Xiaomi’s ultimate goal is the complete transition to solid-state batteries. Liquid components in traditional batteries pose size limitations and rare safety risks. Solid-state technology eliminates these liquids entirely.
Currently in the advanced R&D and prototype stage, Xiaomi’s solid-state batteries aim to break the 1,000 Wh/L energy density barrier. This means future devices will hold drastically more power in much smaller footprints. Initially planned for electric cars (EVs), this technology will eventually make its way into mobile gadgets.
Benefits of upcoming Xiaomi solid-state batteries
-
Massive Energy Density: Significantly higher capacity than lithium-ion.
-
Ultimate Fire Safety: Non-flammable solid electrolytes eliminate fire risks.
-
Extreme Weather Endurance: Highly stable performance even at −20°C.
-
Versatile Applications: The long-term standard for both EVs and mobile tech.
Jinshajiang vs. Solid-State: Feature Comparison
| Feature | Xiaomi Jinshajiang Battery | Xiaomi Solid-State Battery |
| Battery Type | Advanced lithium-ion | Next-generation solid-state |
| Electrolyte Structure | Liquid with elastic polymer | Fully solid electrolyte |
| Anode Material | Silicon-Carbon (Si-C) | Lithium metal (theoretical) |
| Silicon Usage | ~6% (phones), up to 16% (accessories) | None |
| Energy Density | 779 – 843 Wh/L | 1,000+ Wh/L |
| Safety Level | Improved, liquid-based | Very high, minimal fire risk |
| Swelling Risk | Controlled | Nearly eliminated |
| Charge Cycle Life | ~1,600 cycles (80% capacity) | Targeting 1,000+ cycles |
| Production Status | Mass production | R&D / prototype stage |
| Used In | Xiaomi 14 Ultra, Mix Fold series | No commercial products yet |
Xiaomi’s Jinshajiang battery is a massive leap in material science, delivering thinner, longer-lasting batteries today. Meanwhile, their ongoing development of solid-state batteries paves the way for a safer, high-capacity future across the entire tech industry.


 Emir Bardakçı
Emir Bardakçı





what a creative idea.