Xiaomi has changed the way smartphones are made from being assembly line products to fully automated and analytical production lines. Today, Xiaomi phones are made using global supply chain integration and AI-enabled quality control. Whether it’s high-end models such as the Xiaomi 15 line or budget phones, each smartphone undergoes certain standards to be qualified as production-quality items. This guide tells you how a smartphone is made at Xiaomi in detail.
Design, Planning, and Component Sourcing
Before the physical production of the device itself, the company engages in product definition, industrial design, as well as hardware planning. These activities are conducted within the Xiaomi company through research teams in Xiaomi HyperOS.
Xiaomi employs a hybrid model of manufacturing. First, Xiaomi uses ODM manufacturers for most of its entry-level as well as mid-segment phones, whereas it relies upon its smart factory networks in China, known as Xiaomi smart factories, for most of its flagship phones as well as innovations nowadays. In this way, it not only manages cost but also delivers premium qualities.
Key Component Supply Chain
For instance, to minimize risks and ensure smooth production, Xiaomi has a diversified supplier network.
- Proccesors: Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Elite in high-tier smartphones, other tiers by MediaTek
- Displays: TCL CSOT, Samsung Display, BOE, Visionox
- Camera sensors: Sony, OmniVision
- Batteries: ATL, Sun
Such an approach enhances the stability of the supply and the supplies’ price efficiencies while not affecting the quality.
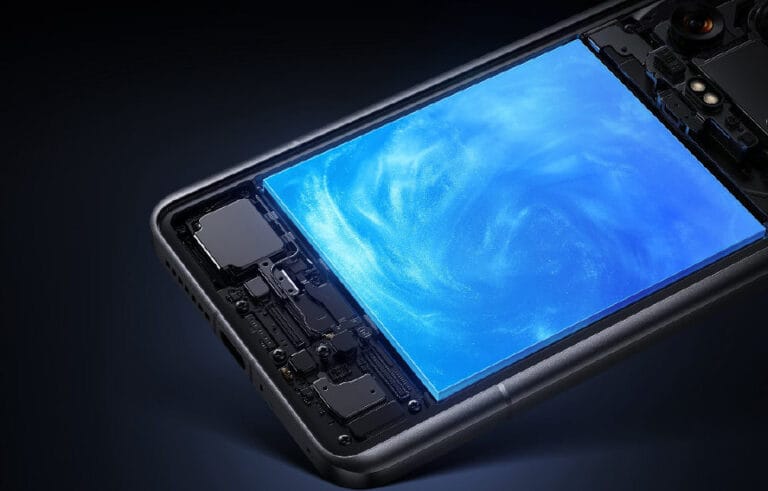
Producing Motherboards and SMT Assembly
The production process kicks off with the manufacturing of the smartphone’s mainboard. This process uses Surface Mount Technology, where thousands of components are placed on a printed circuit by robots.
Solder paste application is followed by high-speed placement of processors, memory, and micro-components by automated machines. Boards are then processed in reflow ovens, where they are bonded using heat. Optical inspection systems, guided by artificial intelligence, verify if there is any error in placement or soldering.
Display Module Assembly & Lamination
One of the costliest and most sensitive parts of a smartphone is the display. The company receives semi-finished units in the form of OLED displays, but finally assembling them in a cleanroom environment.
To begin, the protective glass, known as Dragon Crystal Glass, needs to be made. The joining of the glass and the OLED screen will be done by the use of optically clear adhesive and in a vacuum to prevent air pockets from forming. Once this has been carried out, the screens will be placed in the pressure chamber to get rid of microscopic air pockets.
Final Assembly and Structural Integration
When the basic modules are completed, the phone begins the final assembly stage, called FATP (Final Assembly, Test, and Packaging). Robotics begins assembling the phone’s main board, battery, cameras, speakers, and cooling systems.
The materials with thermal properties and liquid cooling design are applied with high precision. After fastening the internal components, the display and the back panel are sealed with controlled pressure, meeting the requirements for water and dust resistivity rating of IP68.
Software Installation and Calibration
However, the primary function of the device is completed after the hardware is assembled. Xiaomi then embeds the Xiaomi HyperOS onto the device at the factory level. All the devices then get secured identifiers like IMEI and DRM keys.
The phone also undergoes automatic calibration. The displays are color-calibrated, cameras are adjusted and tested, and sensors are ensured for accuracy. All these are aimed at ensuring that all devices are offering a standard experience, irrespective of batch.
The users can later update the system applications on the Xiaomi smartphone using HyperOSUpdates.com or download the MemeOS Enhancer app from Google Play, which also enables the use of hidden features on Xiaomi smartphones.
Quality Control and Reliability Testing
All the Xiaomi phones are tested for quality before they are packaged. The testing includes stress tests, temperature variation tests, button presses, as well as charging simulations.
The devices are also tested for drop strength and exposure to humidity to ensure that they can withstand actual conditions. Any device that does not pass this test is eliminated from the production process.
Xiaomi’s mobile manufacturing is a result of what is achieved when efficiency, robotics, and engineering come together. Xiaomi is able to ensure consistency in product quality by making use of suppliers across the world, as well as AI-enabled manufacturing lines, so that they produce millions of devices a year.



 Emir Bardakçı
Emir Bardakçı